Introduction
Crypto functional tokens are a specific category of cryptocurrencies designed to serve functional roles within blockchain ecosystems. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which primarily function as digital currencies or stores of value, functional tokens are tailored to perform specific tasks or provide access to decentralized services and applications.
Hierarchy in the Crypto Landscape
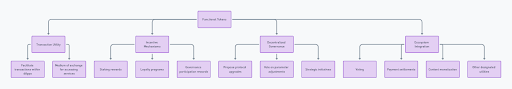
Functional tokens occupy a pivotal position in the crypto hierarchy, bridging user interactions with blockchain applications and protocols. They are foundational to the operational framework of various decentralized platforms, contributing to ecosystem stability and utility.
- Utility Tokens: Provide access to specific products or services within decentralized applications. Examples include tokens used for transaction fees, accessing premium features, or earning rewards.
- Governance Tokens: Empower holders with voting rights and decision-making capabilities within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) or governance frameworks of blockchain protocols.
- Exchange Tokens: Used within cryptocurrency exchanges for trading fee discounts, staking rewards, and other platform-specific benefits.
- Asset-Backed Tokens: Represent physical or digital assets, offering stability and real-world value within blockchain ecosystems.
How Functional Tokens Work
Functional tokens operate based on predefined smart contracts that dictate their behavior and interactions within the blockchain network. Key aspects of how they work include:
- Transaction Utility: Tokens facilitate transactions within dApps, serving as a medium of exchange for accessing services or executing transactions.
- Incentive Mechanisms: Tokens often incorporate incentive structures such as staking rewards, loyalty programs, or governance participation rewards to incentivize user engagement and network participation.
- Decentralized Governance: Governance tokens enable decentralized decision-making by allowing holders to propose and vote on protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, and strategic initiatives.
- Ecosystem Integration: Tokens integrate seamlessly into decentralized ecosystems, supporting functionalities like voting, payment settlements, content monetization, and more, depending on their designated utility.
Characteristics of Crypto Functional Tokens
- Purpose-Driven: Functional tokens are created with specific purposes in mind, such as accessing services, participating in governance, or facilitating transactions within decentralized applications (dApps).
- Smart Contract Integration: They often utilize smart contracts, programmable agreements that automatically execute and enforce the terms of token transactions and interactions within blockchain networks.
- Token Standards: Functional tokens may adhere to standards like ERC-20 (fungible tokens) or ERC-721 (non-fungible tokens, NFTs), depending on their intended functionality and use case requirements.
- Utility and Governance: They can serve various roles:
- Utility Tokens: Used for accessing specific features or services within dApps, such as paying transaction fees or unlocking premium content.
- Governance Tokens: Provide holders with voting rights and influence over decisions within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) or governance frameworks of blockchain protocols.
- Exchange Tokens: Offer benefits like trading fee discounts, staking rewards, and other platform-specific advantages within cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Asset-Backed Tokens: Represent physical or digital assets, providing stability and real-world value within blockchain ecosystems.

Examples of Crypto Functional Tokens
- Basic Attention Token (BAT): Used in the Brave browser ecosystem to reward users for viewing privacy-respecting ads and to compensate content creators based on user engagement.
- Maker (MKR): Empowers governance within the MakerDAO platform, where MKR holders vote on key decisions affecting the Dai stablecoin system, such as collateralization ratios and risk parameters.
- Binance Coin (BNB): Provides utility within the Binance exchange ecosystem, offering discounted trading fees, participation in token sales, and other platform-specific benefits.
Functionality and Use Cases
Crypto-functional tokens enhance blockchain functionality by enabling:
- Efficient Transactions: Facilitating seamless transactions and interactions within decentralized applications.
- Decentralized Governance: Empowering token holders with decision-making capabilities through decentralized governance models.
- Incentive Mechanisms: Implementing reward structures such as staking rewards, governance participation rewards, and loyalty programs to encourage user engagement and network participation.
In summary, crypto-functional tokens play a pivotal role in shaping decentralized ecosystems by providing essential functionalities, governance mechanisms, and utility within blockchain networks. Their structured design and specialized roles contribute to the broader adoption and usability of blockchain technology across various industries and applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, functional crypto tokens represent a transformative element within the blockchain ecosystem, offering diverse applications beyond mere value exchange. These tokens empower users with specific rights and functionalities, enabling innovative use cases across various industries. From enabling decentralized applications and smart contracts to providing governance and utility within ecosystems, functional crypto tokens play a crucial role in driving the adoption and evolution of blockchain technology. As the crypto landscape continues to mature, understanding the distinct roles and potential of functional tokens will be essential for both investors and developers, ensuring informed decisions and fostering further advancements in this dynamic field.