Introduction
Security tokens are digital tokens that represent ownership of real-world assets or financial instruments and are subject to securities regulations. These tokens offer several distinct characteristics, operational mechanisms, functionalities, and use cases within the blockchain ecosystem:
Hierarchy of Security Tokens
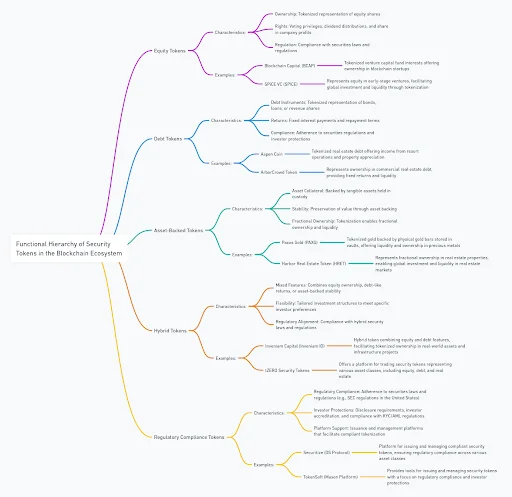
The functional hierarchy of security tokens in the blockchain ecosystem categorizes them based on their primary functions, applications, and the roles they play within digital asset management and investment. Here’s a structured overview of the functional hierarchy of security tokens:
1. Equity Tokens
Equity tokens represent ownership in a company, providing holders with rights similar to traditional equity shareholders, such as voting rights, dividends, and participation in company governance.
- Characteristics:
- Ownership: Tokenized representation of equity shares.
- Rights: Voting privileges, dividend distributions, and share in company profits.
- Regulation: compliance with securities laws and regulations.
- Examples:
- Blockchain Capital (BCAP): Tokenized venture capital fund interests offering ownership in blockchain startups.
- SPiCE VC (SPICE): Represents equity in early-stage ventures, facilitating global investment and liquidity through tokenization.
2. Debt Tokens
Debt tokens represent ownership or rights to debt instruments such as bonds, loans, or revenue-sharing agreements, offering investors fixed income streams and repayment schedules.
- Characteristics:
- Debt Instruments: Tokenized representation of bonds, loans, or revenue shares.
- Returns: Fixed interest payments and repayment terms.
- Compliance: Adherence to securities regulations and investor protections.
- Examples:
- Aspen Coin: Tokenized real estate debt offering income from resort operations and property appreciation.
- ArborCrowd Token: Represents ownership in commercial real estate debt, providing fixed returns and liquidity.
3. Asset-Backed Tokens
Asset-backed tokens are backed by physical assets such as real estate, precious metals, or commodities, offering stability and value through collateralization.
- Characteristics:
- Asset Collateral: Backed by tangible assets held in custody.
- Stability: Preservation of value through asset backing.
- Fractional Ownership: Tokenization enables fractional ownership and liquidity.
- Examples:
- Paxos Gold (PAXG): Tokenized gold backed by physical gold bars stored in vaults, offering liquidity and ownership in precious metals.
- Harbor Real Estate Token (HRET): This token represents fractional ownership in real estate properties, enabling global investment and liquidity in real estate markets.
Secure your Token Platform

4. Hybrid Tokens
Hybrid tokens combine features of equity, debt, or asset-backed tokens, offering diversified investment opportunities and flexible tokenized ownership structures.
- Characteristics:
- Mixed Features: Combines equity ownership, debt-like returns, or asset-backed stability.
- Flexibility: Tailored investment structures to meet specific investor preferences.
- Regulatory Alignment: Compliance with hybrid security laws and regulations.
- Examples:
- Inveniam Capital (Inveniam IO): Hybrid token combining equity and debt features, facilitating tokenized ownership in real-world assets and infrastructure projects.
- tZERO Security Tokens: Offers a platform for trading security tokens representing various asset classes, including equity, debt, and real estate.
5. Regulatory Compliance Tokens
Tokens are specifically designed to comply with securities regulations in different jurisdictions, ensuring legal protection and regulatory compliance for both issuers and investors.
- Characteristics:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to securities laws and regulations (e.g., SEC regulations in the United States).
- Investor Protections: Disclosure requirements, investor accreditation, and compliance with KYC/AML regulations.
- Platform Support: Issuance and management platforms that facilitate compliant tokenization.
- Examples:
- Securitize (DS Protocol): Platform for issuing and managing compliant security tokens, ensuring regulatory compliance across various asset classes.
- TokenSoft (Mason Platform): Provides tools for issuing and managing security tokens with a focus on regulatory compliance and investor protection.
Characteristics of Security Tokens
- Regulation Compliance: Security tokens comply with securities regulations in the jurisdictions where they are offered, providing legal protection and investor rights.
- Asset Backing: They are typically backed by assets such as real estate, equity shares, debt instruments, or revenue-sharing agreements.
- Investor Rights: Holders of security tokens are entitled to dividends, profit shares, voting rights, and other benefits similar to traditional securities.
How Security Tokens Work
Security tokens operate through blockchain technology, utilizing smart contracts to enforce ownership rights, manage compliance with regulatory requirements, and facilitate transactions. Key aspects of how they work include:
- Tokenization: Assets are tokenized, converting ownership rights into digital tokens on a blockchain ledger, enabling fractional ownership and global transferability.
- Legal Compliance: Issuers comply with securities laws and regulations, including registration, disclosure, and investor accreditation requirements, ensuring legal protection and investor confidence.
- Investor Protections: Security tokens provide transparent ownership records, automated dividend distributions, and governance rights through blockchain-based smart contracts.
Functionality and Use Cases
- Equity Tokens:
- Functionality: Represent ownership in companies, providing dividend payments, voting rights, and liquidity through tokenized equity shares.
- Use Cases: Facilitate crowdfunding, venture capital investments, and secondary market trading of private company shares.
- Debt Tokens:
- Functionality: Tokenize debt instruments such as bonds or loans, offering interest payments and repayment schedules to token holders.
- Use Cases: Enhance liquidity in fixed-income markets, streamline loan origination and syndication, and enable fractional ownership of debt securities.
- Real Estate Tokens:
- Functionality: Tokenize ownership in real estate properties, offering rental income, property appreciation, and fractional ownership.
- Use Cases: Increase liquidity in real estate markets, enable global investment in high-value properties, and simplify property management and transactions.
Experience growth with our token sale Just

Examples of Security Tokens
- Blockchain Capital (BCAP):
- Asset: Tokenized venture capital fund interests.
- Functionality: Provides tokenized ownership in a venture capital fund, complying with securities regulations and offering liquidity through secondary market trading.
- SPiCE VC (SPICE):
- Asset: Tokenized equity in startups and early-stage ventures.
- Functionality: Represents ownership in a venture capital fund, facilitating global investment and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Security tokens play a pivotal role in digitizing traditional securities, offering enhanced liquidity, transparency, and accessibility to global investors. Their characteristics, functionalities, and use cases demonstrate their potential to transform capital markets, streamline investment processes, and democratize access to investment opportunities. Understanding security tokens helps stakeholders navigate regulatory complexities, leverage blockchain technology for asset tokenization, and capitalize on innovative financial instruments within the evolving digital economy.